
In BPMN diagrams, pools represent the major participants in a process.
Swimlanes: Containers that separate a set of activities from others, such as pools and lanes. The flows are represented by dashed or straight lines with arrows, while associations use a dotted line to show that specific documents or artifacts are linked to an event or gateway. Connecting objects: Symbols that are used to connect flow objects, such as message flows, sequence flows and associations. For example, an exclusive gateway has only one option for movement, an inclusive gateway has options based on the decision made at the gateway and parallel gateways represent two concurrent tasks in a workflow. Complex processes also include sub-processes and intermediate events, as well as different types of gateways to show how workflow moves through the diagram. 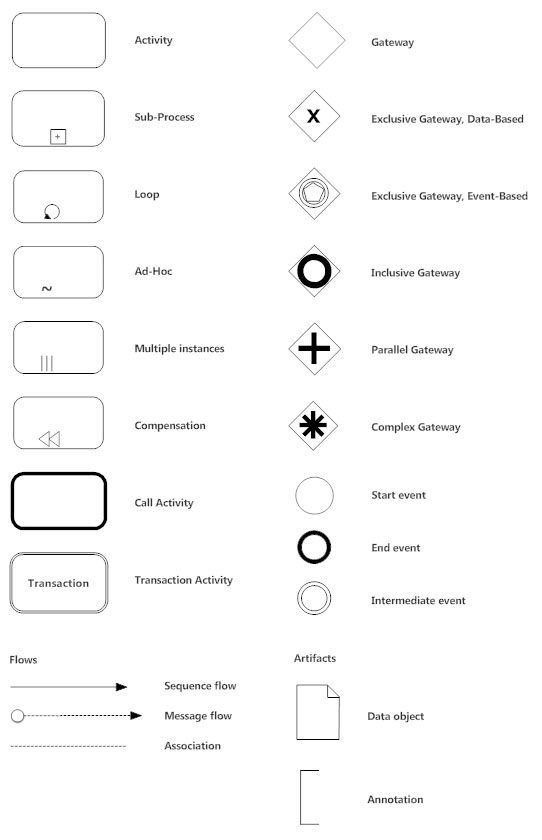
Typically, processes are triggered by a start event, have activities/tasks and gateways (decision points) in the middle and conclude with an end event.
Flow objects: Descriptive objects that are used to define a process, such as events, activities and gateways. The notations are separated into four categories for diagramming: The BPMN language is based on flowcharts and graphical notations. A related XML standard is the Business Process Execution Language (BPEL) for web services. In addition, BPMN diagrams help teams create the XML (Extensible Markup Language) documents needed to execute various processes, such as contract approvals or reminders for monthly financial reports. Create a library of process flows, case definitions and business rules to train new employees. 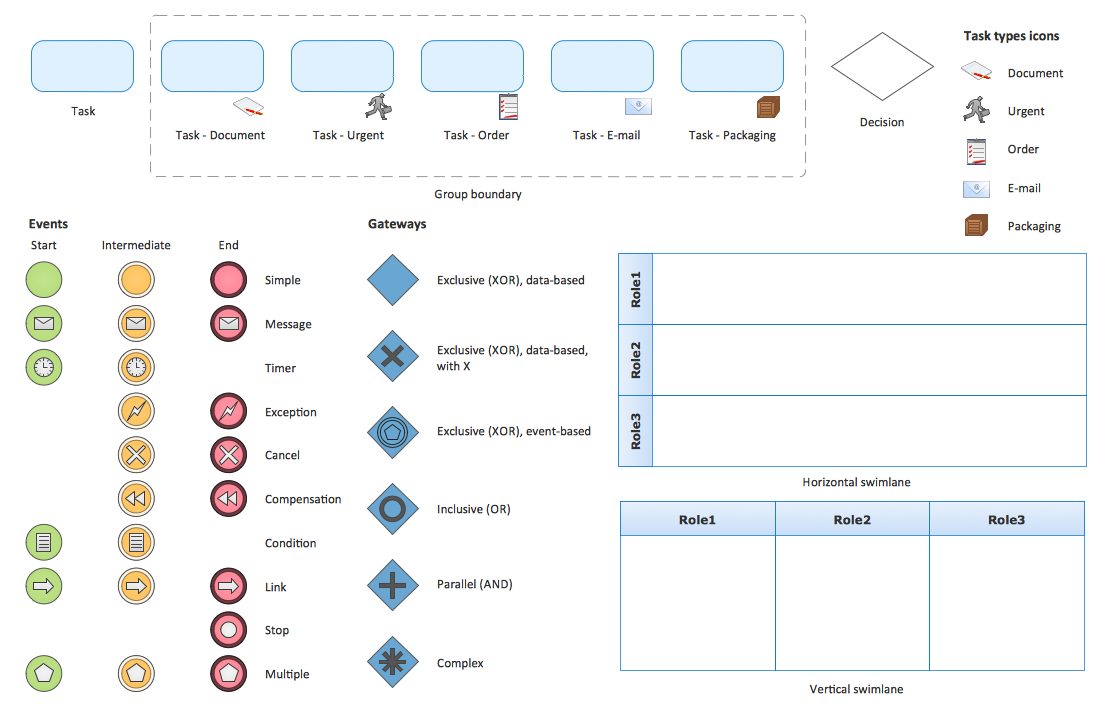 Facilitate the analysis and improvement of operations. Encourage stakeholder participation through graphically expressive notations.
Facilitate the analysis and improvement of operations. Encourage stakeholder participation through graphically expressive notations.  Reach faster agreement on current and future processes through unambiguous models. The BPMN specification is designed to help organizations do the following: This includes the business analysts who create and refine processes, the technical developers responsible for implementing them and the business users who monitor and manage them.
Reach faster agreement on current and future processes through unambiguous models. The BPMN specification is designed to help organizations do the following: This includes the business analysts who create and refine processes, the technical developers responsible for implementing them and the business users who monitor and manage them. 
The value of BPMNīPMN provides a common modeling language that’s readily understandable by all business stakeholders. OMG’s BPMN 2.0.1 specification has been published as International Standard ISO/IEC 19510:2013. The standards differ from unified modeling language (UML) used in software design. The ultimate goal is to help organizations model ways to improve efficiency, account for new circumstances and/or gain a competitive advantage.īPMN 2.0 is part of OMG’s “triple crown” of process improvement standards, which also includes case management model notation (CMMN) and decision model notation (DMN). This open consortium helps ensure that BPMN diagrams can be easily exchanged in a standardized format across different modeling tools. BPMN has been maintained by the Object Management Group (OMG) since 2005.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
